Understanding Plaque Psoriasis
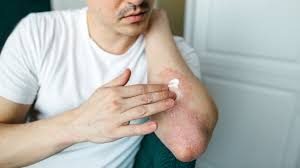
Plaque psoriasis is an autoimmune disease characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the buildup of red, scaly patches on the skin. These plaques are often itchy, painful, and can crack and bleed. The condition is not just a cosmetic issue; it affects overall health and quality of life.
Key Symptoms and Signs
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed or itch.
- Soreness around patches.
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails.
- Swollen and stiff joints.
The Broader Health Implications
Plaque psoriasis is associated with several comorbidities, which makes it a silent threat. These include:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Patients with plaque psoriasis have an increased risk of heart disease.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Chronic inflammation linked with psoriasis raises the risk of insulin resistance.
- Mental Health Issues: The emotional and psychological impact can lead to anxiety and depression.
- Arthritis: Psoriatic arthritis, a condition related to psoriasis, affects the joints and can cause significant disability.
The Data Behind the Threat
Let’s examine the statistics that highlight the seriousness of plaque psoriasis:
| Health Risk | Percentage Increase in Risk |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | 58% |
| Type 2 Diabetes | 46% |
| Depression | 50% |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | 30% |
| Obesity | 22% |
| Metabolic Syndrome | 40% |
| Stroke | 20% |
| Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver | 33% |
| Hypertension | 30% |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 28% |
The data shows a clear connection between plaque psoriasis and a higher incidence of these serious health conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is plaque psoriasis contagious?
A: No, plaque psoriasis is not contagious. It’s an autoimmune condition and cannot be spread through physical contact.
Q: Can plaque psoriasis be cured?
A: There is no cure for plaque psoriasis, but it can be managed with treatment. Therapies aim to reduce inflammation and the rapid turnover of skin cells, thus improving the appearance of skin and overall health.
Q: How is plaque psoriasis diagnosed?
A: A dermatologist typically diagnoses plaque psoriasis through a physical examination and possibly a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
Q: What are the treatment options for plaque psoriasis?
A: Treatment options include topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologics. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and location of the psoriasis, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Q: Does diet impact plaque psoriasis?
A: Yes, diet can influence psoriasis. A healthy diet, rich in anti-inflammatory foods, may help reduce symptoms. Some patients find that eliminating certain foods, such as dairy or gluten, also helps.
Professional Insights
Managing plaque psoriasis involves a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and psychological support. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion
Plaque psoriasis is a complex condition that extends far beyond the skin. Its impact on overall health, including the increased risk of serious diseases, underscores the importance of early detection and comprehensive management. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with plaque psoriasis can better navigate their health challenges and improve their quality of life.
References:







Recent Comments